ax1+bx2=m
cx1+dx2=n
The set has a unique solution
x1=(md-bn)/(ad-cb)
x2=(na-mc)/(ad-cb)
provided ad-cb!=0
Write a program to read the valuues of coefficients and constants a,b,c,d,m,n and compute the value of x1 and x2.
Solution:
1. Algorithm Development :
Step
1 : Start
Step
2 : Read values of a,b,c,d,m,n
Step
3 : Calculate denominator (a*d-c*b)
Step
4 : If Denominator gives value zero, Display Denominator is zero
Step4
: else calculate x1=(m*d-b*n)/denominator
x2=(n*a-m*c)/denominator
Step5:
Display the values of x1 & x2
Step6:
End
2. Flowcharting
3. Coding :
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
float a,b,c,d,m,n,x1,x2,denominator; //Variable Declaration
printf(" Enter the values of a,b and m in ax1+bx2=m \t :");
scanf("%f %f %f",&a,&b,&m);
printf(" Enter the values of c,d and n in cx1+dx2=n \t :");
scanf("%f %f %f",&c,&d,&n);
denominator=a*d-c*b;
if(denominator==0)
printf("\n The Denominator is Zero!!!!");
else
{
x1=(m*d-b*n)/denominator;
x2=(n*a-m*c)/denominator;
printf("\n x1=%.2f\t x2=%.2f",x1,x2);
}
return 0;
} // End of Main Program
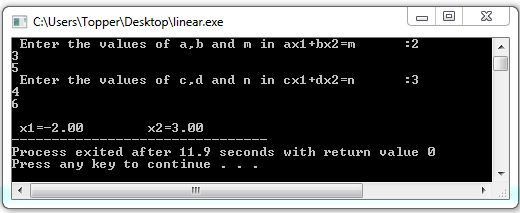
Output :
Output1:
I have used Dev CPP to compile this program.
If you are using Turbo C++ IDE, then use conio.h in link section after stdio.h
and use getch(); to hold the output screen, just before the end of main function.
If you have any confusion regarding the program, please, comment below.
Happy Coding !
Thank you


0 comments:
Post a Comment